Child Maintenance: A Comprehensive Guide for Calculating and Claiming
Child maintenance is a crucial aspect of ensuring the well-being and support of minor children. It encompasses the financial responsibility of providing housing, clothing, food, medical care, education, and other essential needs. Understanding how to calculate child maintenance is essential for both parents to ensure a fair and reasonable contribution. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the court formula used for calculating child maintenance and the steps involved in the process.
The Duty to Maintain: Understanding the Legal Obligations
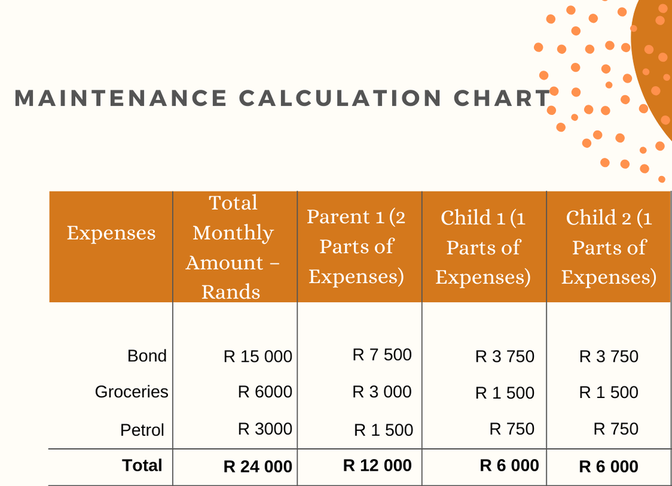
Child maintenance is a legal duty known as "the duty to maintain." It requires parents to contribute to the reasonable needs of their minor children based on their income. The court formula considers the proportionate division of expenses to meet the children's needs. Generally, one part is allocated per child, and two parts per adult living in the same household.
To accurately calculate child maintenance, it is crucial to gather comprehensive information about both parents' income and expenses. This includes salary, bonuses, and income from investments. Additionally, it is essential to consider all expenses, not just the higher amounts, as even small expenses can add up significantly.
Determining the Child's Reasonable Needs
The court formula takes into account the child's reasonable needs, considering factors such as food, clothing, housing, and education. Both parents are expected to contribute to child maintenance according to their means. It is important to note that the child's needs should be assessed based on the family's standard of living. For example, if the child has been attending an expensive private school, the court may consider allowing them to continue attending if it is within the means of the parents.
Let's take a simplified example to demonstrate how child maintenance requirements can be calculated:
The Duty to Maintain: Understanding the Legal Obligations
Child maintenance is a legal duty known as "the duty to maintain." It requires parents to contribute to the reasonable needs of their minor children based on their income. The court formula considers the proportionate division of expenses to meet the children's needs. Generally, one part is allocated per child, and two parts per adult living in the same household.
To accurately calculate child maintenance, it is crucial to gather comprehensive information about both parents' income and expenses. This includes salary, bonuses, and income from investments. Additionally, it is essential to consider all expenses, not just the higher amounts, as even small expenses can add up significantly.
Determining the Child's Reasonable Needs
The court formula takes into account the child's reasonable needs, considering factors such as food, clothing, housing, and education. Both parents are expected to contribute to child maintenance according to their means. It is important to note that the child's needs should be assessed based on the family's standard of living. For example, if the child has been attending an expensive private school, the court may consider allowing them to continue attending if it is within the means of the parents.
Let's take a simplified example to demonstrate how child maintenance requirements can be calculated:
Scenario Details
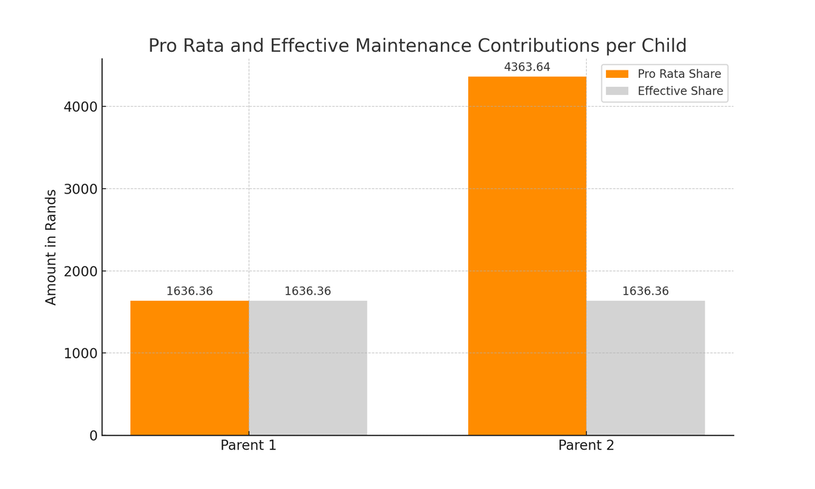
To determine how much Parent 2 should pay to Parent 1 for each child's maintenance, one can apply the pro rata Maintenance Contribution Formula. The formula considers the income of both parents and the needs of the children.
- Parent 1's income: R 15,000
- Parent 2's income: R40,000
- Minor Children's Needs: R 6,000 per child
To determine how much Parent 2 should pay to Parent 1 for each child's maintenance, one can apply the pro rata Maintenance Contribution Formula. The formula considers the income of both parents and the needs of the children.
Maintenance Calculation Formula
It is important to remember that the court will only consider reasonable monthly expenses when calculating child maintenance.
Applying for Child Maintenance: Steps and Procedures
Applying for child maintenance involves several steps to ensure a fair and just outcome. Here is a breakdown of the process:
Child Maintenance Orders: Different Forms and Components
Child maintenance orders can take various forms, depending on the specific circumstances and needs of the children involved. Here are some common components of child maintenance orders:
Additionally, the court may include specific orders related to laying-in expenses, registration of the child as a dependent on a medical aid, or arrear or backdated child maintenance.
Enforcing Child Maintenance Orders and Dealing with Non-Payment
Once a maintenance order is granted, it is legally binding, and failure to comply with the order is a criminal offense. If the non-primary parent fails to pay child maintenance, the primary parent has several options for enforcement:
It is important to note that the primary parent should not withhold access to the child or interfere with visitation rights due to non-payment of child maintenance. Child maintenance and contact with the child are separate matters, and one should not be used as leverage against the other.
Changing Child Maintenance Orders: Increasing or Decreasing Amount
If circumstances change, either the receiving or paying parent can apply to change the child maintenance order. Here are the steps involved:
Both parties will go through a similar process as when initially claiming child maintenance, including court hearings and the consideration of evidence.
Conclusion
Claiming child maintenance and ensuring a fair contribution is crucial for the well-being of minor children. By understanding the court formula for calculating child maintenance and following the necessary steps, parents can navigate the process effectively. It is important to gather comprehensive information about income and expenses, consider the child's reasonable needs, and follow the court's procedures for applying and enforcing child maintenance orders. Remember, child maintenance and contact with the child are separate matters, and both parents have a legal obligation to contribute according to their means.
Download our comprehensive child maintenance calculator by clicking on the download button below.
- The total income of both parents is R 55,000.
- Parent 1's pro rata share for one child's maintenance is approximately R 1,636.36.
- Parent 2's pro rata share for one child's maintenance is approximately R 4,363.64.
It is important to remember that the court will only consider reasonable monthly expenses when calculating child maintenance.
Applying for Child Maintenance: Steps and Procedures
Applying for child maintenance involves several steps to ensure a fair and just outcome. Here is a breakdown of the process:
- Visit the Magistrate's Court: Start by visiting the Magistrate's Court that has jurisdiction over your residential area.
- Obtain and Complete Form A: Obtain and complete Form A, which is the Application for a maintenance order.
- Gather Proof of Income and Expenses: Along with Form A, gather proof of your monthly income and expenses, such as receipts for food purchases, school uniforms, schoolbooks, pharmaceutical items, electricity bills, and rent payments.
- Court Set Date: The court will set a date for both parties involved, the applicant and the respondent, to be present.
- Maintenance Investigator: The court may appoint a Maintenance Investigator to examine the claim and gather additional information about the respondent's income and expenses.
- Maintenance Subpoena: The court will serve a Maintenance Subpoena on the respondent, requiring them to appear in court on the specified date.
- Consent or Contest: The respondent can either agree to pay the maintenance or contest the matter in court.
- Section 6 and Section 10 Enquiries: If the respondent agrees to pay, a magistrate will review the documentation and make an order. If the respondent contests, both parties will present evidence during the section 6 and section 10 enquiries, respectively.
- Maintenance Order: If the court finds the respondent liable for maintenance, it will make an order for the payment of maintenance.
- Payment Methods: The court can order the maintenance money to be paid through various methods, such as at the local magistrate's office, into a designated bank account, directly to the recipient, or through the deduction from the respondent's salary.
Child Maintenance Orders: Different Forms and Components
Child maintenance orders can take various forms, depending on the specific circumstances and needs of the children involved. Here are some common components of child maintenance orders:
- Cash Components: The non-primary parent may be required to make monthly cash contributions to the primary parent to support the child financially.
- Education and School Payments: Child maintenance payments may cover the cost of attending school, including expenses related to aftercare, lunch, outings, books, stationery, uniforms, and sports activities.
- Medical Expenses: Child maintenance may also include the cost of medical care, including medical aid coverage for the child.
Additionally, the court may include specific orders related to laying-in expenses, registration of the child as a dependent on a medical aid, or arrear or backdated child maintenance.
Enforcing Child Maintenance Orders and Dealing with Non-Payment
Once a maintenance order is granted, it is legally binding, and failure to comply with the order is a criminal offense. If the non-primary parent fails to pay child maintenance, the primary parent has several options for enforcement:
- Warrant of Execution: The primary parent can obtain a warrant of execution, which allows for the seizure of the non-paying parent's property or the attachment of their emoluments (garnishee order) or debt.
- Complaint to Maintenance Court: If the non-paying parent continues to neglect their child maintenance obligations, the primary parent can lodge a complaint with the Maintenance Court. A maintenance officer will investigate the complaint, and if necessary, the court may issue a garnishee order against the non-paying parent's salary.
It is important to note that the primary parent should not withhold access to the child or interfere with visitation rights due to non-payment of child maintenance. Child maintenance and contact with the child are separate matters, and one should not be used as leverage against the other.
Changing Child Maintenance Orders: Increasing or Decreasing Amount
If circumstances change, either the receiving or paying parent can apply to change the child maintenance order. Here are the steps involved:
- Application for Change: The receiving parent must apply at the Magistrate's Court in the area where the paying parent resides. They need to complete the relevant application form and submit it to the maintenance officer, along with a list of their income and expenses.
- Request for Decrease: If the paying parent can no longer afford the maintenance amount due to changed circumstances, they can also apply at the Magistrate's Office in the area where the receiving parent resides. They need to complete the application form, provide a list of income and expenses, and submit a written explanation for the request.
Both parties will go through a similar process as when initially claiming child maintenance, including court hearings and the consideration of evidence.
Conclusion
Claiming child maintenance and ensuring a fair contribution is crucial for the well-being of minor children. By understanding the court formula for calculating child maintenance and following the necessary steps, parents can navigate the process effectively. It is important to gather comprehensive information about income and expenses, consider the child's reasonable needs, and follow the court's procedures for applying and enforcing child maintenance orders. Remember, child maintenance and contact with the child are separate matters, and both parents have a legal obligation to contribute according to their means.
Download our comprehensive child maintenance calculator by clicking on the download button below.